Page 115 WHO - Guidelines on the pharmacological treatment of persisting pain in children with medical illness
P. 115
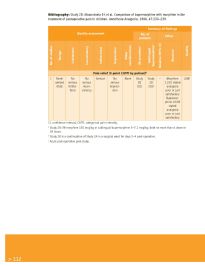
Bibliography: Study 2B: Maunuksela E-l et al. Comparison of buprenorphine with morphine in the
treatment of postoperative pain in children. Anesthesia Analgesia, 1988, 67:233–239.
Summary of findings
Quality assessment No. of
patients Effect
No. of studies Design Limitations Inconsistency Indirectness Imprecision Other considerations IM morphine a Sublingual buprenorphine a Relative (95% CI) Absolute Quality
Pain relief (5 point CATPI by patient) b
2 Rand- No No Serious c No None Study Study – Morphine LOW
omized serious serious serious 2B 2B 11/32 stated
trials limita- incon- impreci- (32) (28) analgesia
tions sistency sion poor or just
satisfactory
Buprenor-
phine 10/28
stated
analgesia
poor or just
satisfactory
CI, confidence interval; CATPI, categorical pain intensity.
a Study 2B: IM morphine 150 mcg/kg or sublingual buprenorphine 5–7.1 mcg/kg; both no more than 6 doses in
24 hours.
b Study 2B is a continuation of Study 2A in a surgical ward for days 2–4 post-operative.
c Acute post-operative pain study.
> 112