Page 201 Acute Pain Management
P. 201
Source: Bandolier (www.medicine.ox.ac.uk/bandolier). Reproduced with permission.
6.1.1 Opioids and tramadol
Oral opioids can be as effective in the treatment of acute pain as opioids given by other more
invasive routes if equianalgesic doses are administered. Both immediate‐release (IR) and CR
formulations have been used. When opioids are prescribed for the treatment of acute pain,
consideration should be given to duration of therapy. In most cases short‐term use only of
these drugs is warranted. Discharge planning must take into account the duration of use of
opioids prescribed for the short‐term management of acute pain and the weaning of those CHAPTER 6
drugs and, in a small minority of patients, the potential for prescribed opioids to be abused or
misused.
Immediate-release formulations
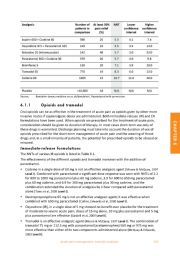
The NNTs of various IR opioids is listed in Table 6.1.
The effectiveness of the different opioids and tramadol increases with the addition of
paracetamol.
• Codeine in a single dose of 60 mg is not an effective analgesic agent (Moore & McQuay, 1997
Level I). Combined with paracetamol a significant dose response was seen with NNTs of 2.2
for 800 to 1000 mg paracetamol plus 60 mg codeine, 3.9 for 600 to 650 mg paracetamol
plus 60 mg codeine, and 6.9 for 300 mg paracetamol plus 30 mg codeine, and the
combination extended the duration of analgesia by 1 hour compared with paracetamol
alone (Toms et al, 2009 Level I).
• Dextropropoxyphene 65 mg is not an effective analgesic agent; it was effective when
combined with 650 mg paracetamol (Collins, Edwards et al, 2000 Level I).
• Oxycodone (IR), in a single dose of 5 mg showed no benefit over placebo for the treatment
of moderate to severe acute pain; doses of 15 mg alone, 10 mg plus paracetamol and 5 mg
plus paracetamol are effective (Gaskell et al, 2009 Level I).
• Tramadol is an effective analgesic agent (Moore & McQuay, 1997 Level I). The combination of
tramadol 75 mg or 112.5 mg with paracetamol (acetaminophen) 560 mg or 975 mg was
more effective than either of its two components administered alone (McQuay & Edwards,
2003 Level I).
Acute pain management: scientific evidence 153